The Indian stock market has grown rapidly in the past decade, attracting millions of new investors. One of the most exciting opportunities for both companies and investors is the Initial Public Offering (IPO). Whether you are a first-time investor or someone looking to understand how companies go public, this guide will walk you through everything about IPOs in India — from the basics, benefits, and process to risks, regulations, and tips for investors.
What is an IPO in India?
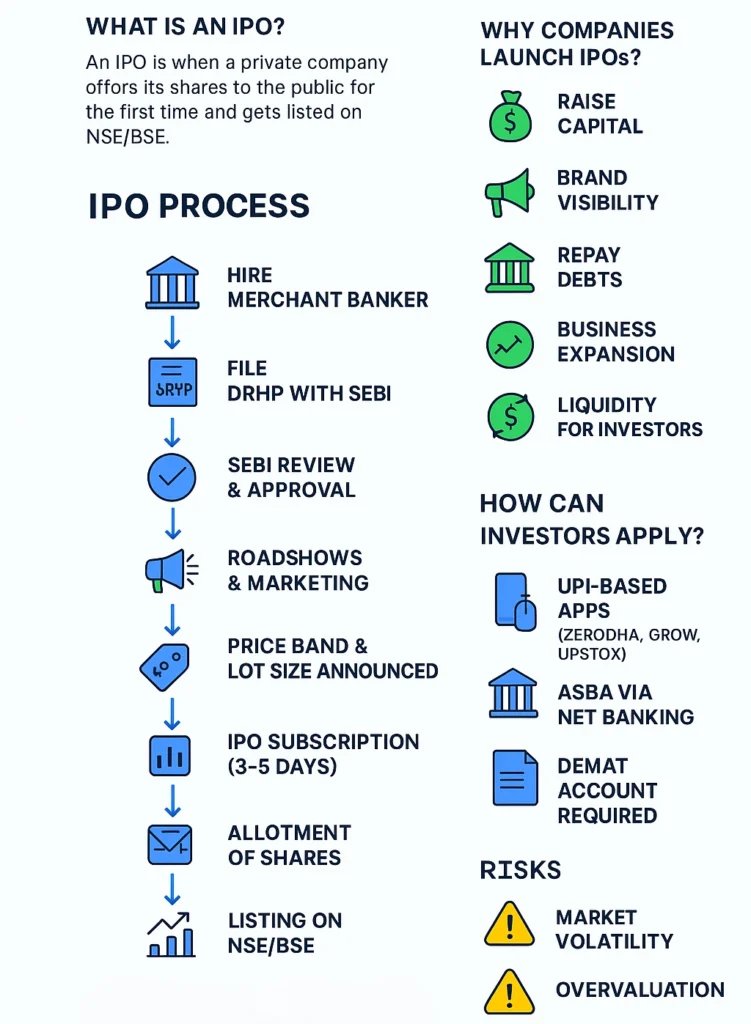
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the process by which a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time and becomes listed on a stock exchange like the NSE (National Stock Exchange) or BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange).
Through an IPO, companies raise capital for expansion, debt repayment, or business growth, while investors get a chance to own equity in the company at an early stage.
Why Do Companies Launch IPOs?
Companies in India choose to launch IPOs for multiple reasons:
- Capital for Growth: To fund new projects, acquisitions, or business expansion.
- Debt Repayment: Raising money to reduce financial liabilities.
- Brand Visibility: Being listed improves credibility and public image.
- Liquidity for Promoters & Early Investors: Allows founders and venture capitalists to partially exit and monetize their investments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Public listing can help in meeting corporate governance standards.
Types of IPOs in India
There are two main types of IPOs:
- Fixed Price IPO – The company sets a fixed price for shares before the issue opens.
- Book-Building IPO – A price band is set, and investors bid within this range. The final price is determined based on demand.
Most modern IPOs in India use the book-building method, as it provides fairer price discovery.
The IPO Process in India (Step by Step)
The IPO process in India is strictly regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to ensure transparency. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Appointment of Merchant Banker
Companies hire investment banks (merchant bankers) to act as lead managers for the IPO.
2. Filing of Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP)
The company prepares a DRHP containing details about financials, business model, risks, and objectives. This is submitted to SEBI.
3. SEBI Review and Approval
SEBI examines the DRHP and gives observations. Only after approval can the IPO move forward.
4. Roadshows and Investor Marketing
The company, along with merchant bankers, conducts roadshows to generate investor interest.
5. Price Band and Lot Size Announcement
The issuer decides the price band (e.g., ₹100–₹110 per share) and the minimum lot size (e.g., 50 shares).
6. IPO Subscription (Bidding Period)
The IPO is open for subscription (usually 3 days). Investors apply through banks, stockbrokers, or apps like Zerodha, Groww, and Upstox.
7. Allotment of Shares
Based on demand and availability, shares are allotted. If the IPO is oversubscribed, allotment is done via lottery for retail investors.
8. Listing on Stock Exchange
Once allotment is complete, the company’s shares are listed on NSE and BSE. Investors can buy and sell shares freely after listing.
How Can Retail Investors Apply for an IPO in India?
Retail investors can apply for IPOs using:
- ASBA (Application Supported by Blocked Amount) through net banking.
- UPI-based Applications on broker platforms like Zerodha, Angel One, and Groww.
- Demat Account is mandatory since IPO shares are credited electronically.
Example: A Recent IPO in India
For instance, the LIC IPO (2022) was the largest ever in India, raising over ₹21,000 crore. It allowed millions of retail investors, including policyholders, to participate in India’s biggest insurance company’s growth journey.
Benefits of Investing in IPOs
- Early Entry Advantage: Buying shares before they trade freely.
- Potential Listing Gains: Many IPOs list at a premium, giving immediate profits.
- Long-Term Wealth Creation: Investing in fundamentally strong IPOs can yield high returns over time (e.g., Infosys, TCS, HDFC Bank).
Risks of Investing in IPOs
- Market Volatility: Listing price may fall below the issue price.
- Overvaluation Risk: Sometimes companies are priced too high.
- Uncertain Business Models: New companies may lack proven track records.
👉 Tip: Always read the prospectus, study financials, and check industry trends before investing.
Regulatory Role of SEBI in IPOs
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) ensures:
- Transparency in disclosures.
- Protection of retail investors.
- Fair allotment process.
- Strict compliance with guidelines.
Upcoming IPO Trends in India
With India’s growing economy, more startups and established firms are planning IPOs. Sectors like fintech, renewable energy, and consumer tech are expected to dominate IPO activity in the coming years.
FAQs About IPOs in India
1. What is an IPO in simple words?
An IPO is when a private company sells its shares to the public for the first time and gets listed on a stock exchange.
2. How can I apply for an IPO in India?
You can apply through your bank’s net banking (ASBA) or via stockbroker apps using your UPI and Demat account.
3. How is IPO allotment decided?
For retail investors, allotment is usually done through a lottery system if the issue is oversubscribed.
4. Is IPO investment risk-free?
No. While IPOs can give high returns, they also carry risks. Proper research is essential.
5. What happens if I don’t get IPO allotment?
If shares are not allotted, your blocked money is automatically released by the bank.
Final Thoughts
An IPO in India is more than just a fundraising event — it’s a gateway for companies to grow and for investors to participate in their journey. While IPOs can be highly rewarding, they also come with risks. Investors should evaluate the company’s fundamentals, business model, and long-term prospects before applying.
With SEBI’s strict regulatory framework, the IPO process in India is structured to protect investors and ensure fairness. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned trader, understanding how IPOs work will help you make smarter investment decisions.


